What is LPWAN?
Let’s start with the abbreviation: WAN. WAN simply stands for a Wide Area Network. In other words a network that encompasses a wide area such as a town, a city, a state, a county, a country are all called WANs. Eg: Your cellular network is a WAN, the internet we seamlessly use to communicate is also a WAN. Your landline is also a part of the WAN. That said, unless your landline is battery operated and has a really long battery life you cannot take it and move around. Hence to make the WAN truly scalable you need it to be low powered: LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network)
LPWANs use wireless communications to link devices together over very long ranges using very low power signals. A major drawback of LPWAN is that they are too slow when compared to your home Wi-Fi or mobile data networks such as 4G. A couple of LPWANs can manage close to 125KB/s per channel, and the slowest operate at around 12B/s. This drawback is, however, acceptable because the size of the payload is really low and the focus is more on the longer battery life. Eg: Many LPWAN networks connect battery-operated sensors that are miles apart and have to run for years between battery changes to be practical.
What are the types of LPWANs?
The following types of LPWANs exist today:
Popular Cellular network based LPWANs
- NB IoT
- LTE M / CAT M1
Popular Non Cellular network based LPWANs
- LoRa
- SigFox
- Weightless
Cellular network based LPWANs:
Out of both the LPWANs here the most popular is LTE-M, which uses smartphone infrastructure, making it a very wide network indeed. The ‘M’ is standing in for MTC (Machine Type Communication) over the LTE standard cell phone infrastructure. LTE-M networks operate at the high end in terms of bitrate at up 125KB/s.
Telecom providers can make LTE-M LPWAN gateways out of their cellular towers by adding a bit of software – no new hardware needed. In India none of the major cellular network providers currently provide an LTE-M network/gateways to its customers.
NB-IoT stands for Narrowband Internet of Things, and it does just what it stands for. It has perhaps a quarter the maximum bitrate of the LTE-M systems at around ~30KB/s, and it does not use the LTE in the same way mobile devices do. It relies on DSSS modulation instead. It can be used on LTE bands, or on GSM bands at around 180 kHz.
NB-IoT, interestingly, does not require a gateway. Devices can send data directly to the server, if the other physical and data infrastructure is in place. It is also considered a very reliable protocol, so it is preferred for high priority monitoring applications. It also requires dramatically less power to operate than LTE-M.
More information on the comparison between NBIoT and LTE-M will follow in the upcoming articles.
Non cellular network based LPWANs:
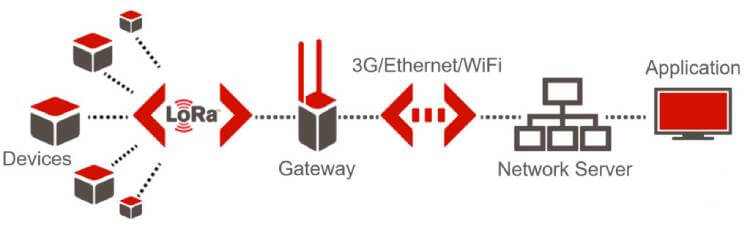
Out of the three LPWANs the most popular is LoRa also known as LoRaWAN. The LoRaWAN® specification is a Low Power, Wide Area (LPWA) networking protocol designed to wirelessly connect battery operated ‘things’ to the internet in regional, national or global networks, and targets key Internet of Things (IoT) requirements such as bi-directional communication, end-to-end security, mobility and localization services.
SigFox, is another popular LPWAN network. Sigfox has designed its technology and network to meet the requirements of mass IoT applications; long device battery life-cycle, low device cost, low connectivity fee, high network capacity, and long range. A device is not attached to a specific base station unlike cellular protocols. The broadcasted message is received by any base station in the range, which is 3 in average.
Also gaining popularity is another protocol called Weightless originally written by a company called Ubiik. Weightless technology delivers wireless connectivity for low power, wide area networks (LPWAN) specifically designed for the Internet of Things. Weightless can operate in both sub-1GHz licence exempt and licensed spectrum. The Weightless SIG is a non-profit, interestingly enough. They have made Weightless and open standard, ideally to increase uptake and innovation. However, it isn’t very popular, and there is not a lot of hardware available. The one exception is the Nwave smart parking company, they use a proprietary version of the old Weightless N standard which is very widespread.
Want to learn more? The experts at Ambimat Electronics can help with all the details, including choosing the solution that’s best for you. Reach out to us on our contact us page
About Ambimat Electronics:
With design experience of close to 4 decades of excellence, world-class talent, and innovative breakthroughs, Ambimat Electronics is a single-stop solution enabler to Leading PSUs, private sector companies, and start-ups to deliver design capabilities and develop manufacturing capabilities in various industries and markets. AmbiIoT design services have helped develop Smartwatches, Smart homes, Medicals, Robotics, Retail, Pubs and brewery, Security.
Ambimat Electronics has come a long way to become one of India’s leading IoT(Internet of things) product designers and manufacturers today. We present below some of our solutions that can be implemented and parameterized according to specific business needs. AmbiPay, AmbiPower, AmbiCon, AmbiSecure, AmbiSense, AmbiAutomation.
To know more about us or what Ambimat does, we invite you to follow us on LinkedIn or visit our website.
References:-
https://www.rutronik.com/article/detail/News/low-power-wide-area-networks-lpwan-advantages-and-disadvantages-of-the-leading-narrow-band-iot-an/
https://blog.mxc.org/benefits-limitations-lpwan/
https://www.sigfox.com/en/what-sigfox/technology#id_technology
https://lora-alliance.org/about-lorawan