Dear Readers,
This week’s blog is how a biometric passport is expected to enable technological advancement? What is the Most Important Application of e-passport or biometric identification card?
Ambimat Electronics, with its experience of over four decades as an ODM of IoT products, wishes to draw the attention of its customers and readers of blog posts towards this upcoming field.
What is an e-passport?
With a chip embedded in it, the e-passport will ensure the security of the passport holder’s data. The chip in the e-passport adds advanced security features to it. With the security features, if anyone tries to tamper with the chip, the system will be able to detect it. Moreover, it can’t be tampered with and the misuse of the passport will be prevented.
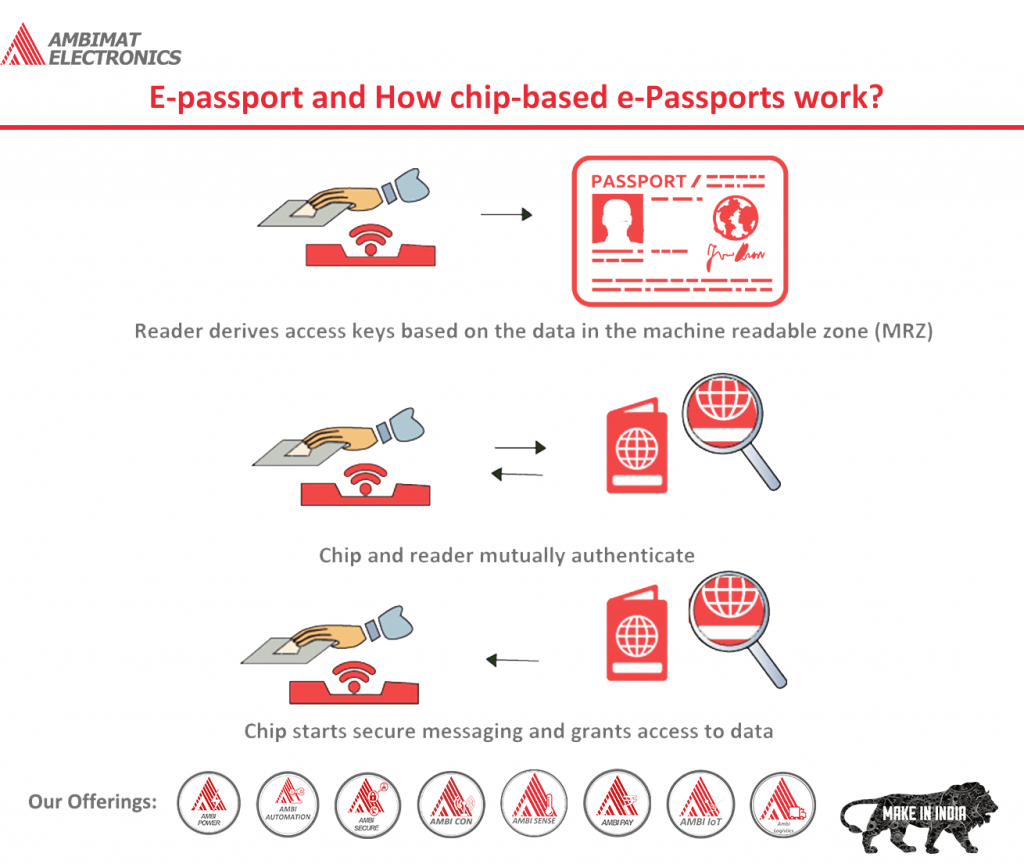
Introduction
A biometric passport (also known as an e-passport, ePassport, or a digital passport) is a traditional passport that has an embedded electronic microprocessor chip that contains biometric information that can be used to authenticate the identity of the passport holder. It uses contactless smart card technology, including a microprocessor chip (computer chip) and antenna (for both power to the chip and communication) embedded in the front or back cover, or center page, of the passport. The passport’s critical information is printed on the data page of the passport, repeated on the machine-readable lines, and stored in the chip. Public key infrastructure (PKI) is used to authenticate the data stored electronically in the passport chip, making it expensive and difficult to forge when all security mechanisms are fully and correctly implemented.
Many countries are moving towards issuing biometric passports to their citizens. Malaysia was the first country to issue biometric passports in 1998. In December 2008, 60 countries were issuing such passports, which increased to 120 by June 2017.
The currently standardized biometrics used for this type of identification system are facial recognition, fingerprint recognition, and iris recognition. These were adopted after the assessment of several different kinds of biometrics including retinal scan. Document and chip characteristics are documented in the International Civil Aviation Organization’s (ICAO) Doc 9303 (ICAO9303). The ICAO defines the biometric file formats and communication protocols to be used in passports. Only the digital image (usually in JPEG or JPEG2000 format) of each biometric feature is actually stored in the chip. The comparison of biometric features is performed outside the passport chip by electronic border control systems (e-borders). To store biometric data on the contactless chip, it includes a minimum of 32 kilobytes of EEPROM storage memory and runs on an interface in accordance with the ISO/IEC 14443 international standard, amongst others. These standards intend interoperability between different countries and different manufacturers of passport books.
Some national identity cards, such as those from the Netherlands, Albania, and Brazil, are fully ICAO9303 compliant biometric travel documents. However, others, such as the United States Passport Card, are not.
An e-passport is a biometric identification card that comes embedded with an electronic chip that holds the same information as printed on the passport’s data page such as the holder’s name, date of birth, and other details.
The biometric data of an individual is also saved in the chip. The e-passport will help passengers do away with the hassle of standing in long queues at the immigration counters as it can be scanned within a few minutes.
The government believes that biometric passports will help check the menace of frauds and fake passports as it will be difficult for fraudsters to change data recorded on it. How? Well, passport authentication will fail if anyone tries to tamper with the chip. An e-passport is also designed in a way that the data on it cannot be wiped remotely.
What are the salient features?
1) Digitally signed, the chip in the e-passport will have the personal particulars of the applicant.
2) For better protection, the e-passport will have thicker back and frontier covers.
3) It will facilitate the passengers while traveling as the e-passport will help save time at immigration counters because it will take only a second to read.
4) In the 1-passport, data on up to 30 international visits will be stored in the chip with a memory space of 64 kilobytes.
The AmbiPay device can be used in any field that is dependent on the ability to reliably and securely readout identity documents or to verify their authenticity. Passport producers and authorities responsible for issuing identity documents can check the function and data of the document before dispatch; Stationary and mobile border controls can use the AmbiPay to verify passports and electronic residence permits; Security authorities can identify forged passports. AmbiPay Opens Numerous functions, adaptable design, diversity of applications
About Ambimat Electronics:
With design experience of close to 4 decades of excellence, world-class talent, and innovative breakthroughs, Ambimat Electronics is a single-stop solution enabler to Leading PSUs, private sector companies, and start-ups to deliver design capabilities and develop manufacturing capabilities in various industries and markets. AmbiIoT design services have helped develop Smartwatches, Smart homes, Medicals, Robotics, Retail, Pubs and brewery, Security.
Ambimat Electronics has come a long way to become one of India’s leading IoT(Internet of things) product designers and manufacturers today. We present below some of our solutions that can be implemented and parameterized according to specific business needs. AmbiPay, AmbiPower, AmbiCon, AmbiSecure, AmbiSense, AmbiAutomation.
To know more about us or what Ambimat does, we invite you to follow us on LinkedIn or visit our website.
Reference:-
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biometric_passport
https://www.internationalairportreview.com/article/1411/epassports-examining-the-benefit/